Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
HOMO and LUMO
HOMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) and LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) are key concepts in molecular orbital theory. The HOMO is the highest energy orbital that contains electrons, while the LUMO is the lowest energy orbital that is empty. The energy gap between these two orbitals is crucial for understanding the reactivity of molecules, as it influences how they interact with other species.
Recommended video:
Allylic Cation and Anion
An allylic cation is a positively charged species where the positive charge is located on a carbon atom adjacent to a double bond, while an allylic anion has a negative charge on a similar carbon atom. These species are important in organic chemistry due to their stability and reactivity, which can be analyzed through their molecular orbitals. The resonance stabilization in these structures significantly affects their HOMO and LUMO energies.
Recommended video:
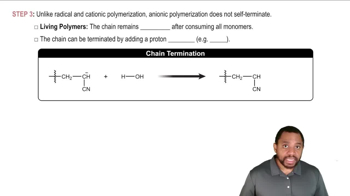
Anionic Polymerization Concept 4
Resonance
Resonance is a concept used to describe the delocalization of electrons in molecules that can be represented by two or more valid Lewis structures. In the case of allylic cations and anions, resonance allows for the distribution of charge over multiple atoms, which stabilizes the species. Understanding resonance is essential for predicting the behavior of these ions, including the characteristics of their HOMO and LUMO.
Recommended video:
Drawing Resonance Structures
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:35m
2:35m