Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amines
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of carbon-containing groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Understanding the structure and classification of amines is essential for drawing their condensed and skeletal forms.
Recommended video:
Condensed Structures
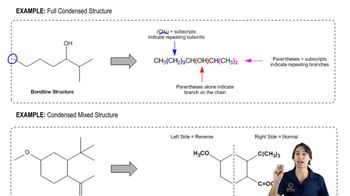
Condensed structures are a simplified way of representing molecular structures where bonds are implied rather than explicitly drawn. In these structures, atoms are listed in a linear format, showing how they are connected without depicting every bond. For amines, the condensed structure will show the nitrogen atom bonded to its substituents, providing a clear view of the molecular composition.
Recommended video:
How to interpret condensed structures.
Skeletal Structures
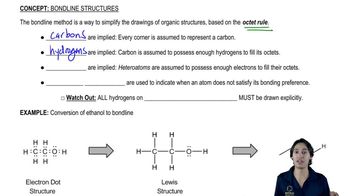
Skeletal structures, also known as line-angle structures, are a shorthand representation of organic molecules where carbon atoms are represented by vertices and hydrogen atoms are often omitted for clarity. Each vertex represents a carbon atom, and the bonds are drawn as lines. This method is particularly useful for visualizing larger molecules like amines, as it simplifies the depiction of complex structures.
Recommended video:
How bondline is different from Lewis Structures.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution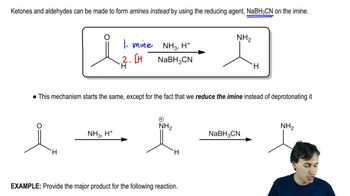

 6:50m
6:50m