Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Integration in NMR Spectroscopy
Integration in NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) spectroscopy refers to the area under the peaks in an NMR spectrum, which correlates to the number of protons contributing to that signal. This allows chemists to determine the relative number of hydrogen atoms in different environments within a molecule, aiding in structure elucidation.
Recommended video:
Multiplicity in NMR Spectroscopy
Multiplicity in NMR spectroscopy describes the splitting pattern of NMR signals, which arises from the interaction of neighboring hydrogen atoms (spin-spin coupling). The number of peaks observed (singlet, doublet, triplet, etc.) provides insight into the number of adjacent protons, helping to deduce the connectivity and arrangement of atoms in the molecule.
Recommended video:
Alkyl Groups and Their NMR Patterns
Alkyl groups, such as isopropyl, exhibit characteristic NMR patterns based on their structure. For isopropyl, the NMR spectrum typically shows a singlet for the methyl protons and a multiplet for the methine proton due to its neighboring methyl groups, allowing for the identification of the isopropyl structure through its unique integration and multiplicity.
Recommended video:
Common Splitting Patterns
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution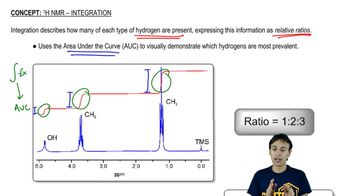



 6:46m
6:46m