Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cis-Trans Isomerism
Cis-trans isomerism refers to the different spatial arrangements of atoms in a molecule that can occur due to restricted rotation around a double bond or a ring structure. In the case of cyclopropane derivatives, the 'cis' isomer has substituents on the same side of the ring, while the 'trans' isomer has them on opposite sides. This spatial arrangement affects steric interactions and overall stability.
Recommended video:
Is the following cyclohexane cis or trans?
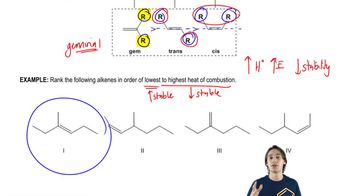
Heat of Combustion
The heat of combustion is the amount of energy released when a substance is completely burned in oxygen. It serves as an indicator of the stability of a compound; a higher heat of combustion typically suggests that the compound is less stable, as it releases more energy upon combustion. Thus, comparing the heats of combustion of isomers can provide insights into their relative stabilities.
Recommended video:
Stability and Strain in Cyclopropanes
Cyclopropanes are known for their ring strain due to the 60-degree bond angles that deviate significantly from the ideal tetrahedral angle of 109.5 degrees. This strain can be influenced by the arrangement of substituents in cis and trans isomers. The trans isomer generally experiences less steric hindrance and strain, making it more stable than the cis isomer, which has increased steric interactions between substituents.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:11m
1:11m