Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aziridine Structure
Aziridine is a three-membered cyclic amine with one nitrogen atom and two carbon atoms. The '2-methyl' designation indicates a methyl group attached to the second carbon of the aziridine ring. Understanding the geometry and bonding in small rings is crucial for accurately drawing aziridine derivatives.
Recommended video:
Drawing Resonance Structures
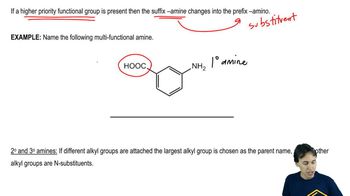
Amine Nomenclature
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. The naming convention for amines includes identifying the longest carbon chain and the substituents, as seen in 'N-ethyl-N-methylhexan-3-amine,' which indicates a hexane backbone with ethyl and methyl groups attached to the nitrogen.
Recommended video:
Primary Amines as Substituents
Substituent Positioning
In organic chemistry, the position of substituents on a carbon chain is critical for understanding the compound's structure and reactivity. For example, 'm-chloroaniline' refers to a chloro group positioned meta to the amino group on a benzene ring. Recognizing how to interpret and depict these positions is essential for accurate structural representation.
Recommended video:
Reactions at the Allylic Position Example 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 6:50m
6:50m