Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It relies on the magnetic properties of certain nuclei, such as hydrogen, to provide information about the environment surrounding these nuclei. In NMR, the splitting patterns of signals indicate the number of neighboring protons, which is crucial for understanding coupling interactions.
Recommended video:
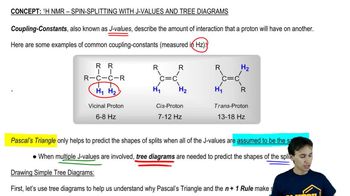
Coupling Constants and Spin-Spin Splitting
Coupling constants arise from the interaction between neighboring nuclear spins, leading to spin-spin splitting in NMR spectra. The degree of splitting is influenced by the number of adjacent protons and their spatial arrangement. In the case of cis and trans alkenes, certain protons may not couple due to their geometric arrangement, resulting in distinct NMR signals.
Recommended video:
Splitting with J-Values:Simple Tree Diagram
Geometric Isomerism in Alkenes
Geometric isomerism occurs in alkenes due to restricted rotation around the double bond, leading to cis and trans configurations. In cis isomers, substituents are on the same side, while in trans isomers, they are on opposite sides. This spatial arrangement affects the coupling of protons in NMR, as protons that are not in close proximity or are in a different spatial orientation do not couple, leading to the absence of certain splitting patterns.
Recommended video:
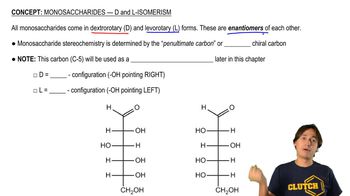
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 12:21m
12:21m