Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aldohexoses
Aldohexoses are a class of carbohydrates that contain six carbon atoms and an aldehyde functional group. They are a subset of monosaccharides and include sugars like glucose, galactose, and mannose. Understanding their structure and reactivity is essential for identifying which aldohexose can be oxidized to d-glucaric acid.
Recommended video:
Which aldohexoses produce the same Wohl Degradation product
Oxidation Reactions
Oxidation reactions involve the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule. In organic chemistry, this often refers to the conversion of alcohols to carbonyls or carboxylic acids. In the context of aldohexoses, nitric acid acts as an oxidizing agent, converting specific sugars into their corresponding acids, such as d-glucaric acid.
Recommended video:
D-Glucaric Acid
D-glucaric acid, also known as saccharic acid, is a dicarboxylic acid derived from the oxidation of aldohexoses. It is important in biochemistry and has applications in pharmaceuticals and detoxification processes. Recognizing its alternative name can aid in understanding its chemical properties and biological significance.
Recommended video:
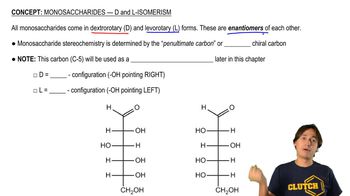
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution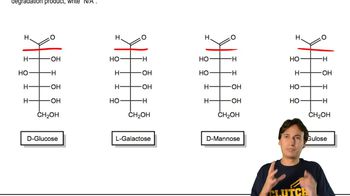


 3:10m
3:10m