Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pericyclic Reactions
Pericyclic reactions are a class of organic reactions that occur through a concerted mechanism, involving a cyclic transition state. These reactions typically involve the rearrangement of electrons in a way that conserves orbital symmetry, allowing for the simultaneous breaking and forming of bonds. Common types include electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions, and sigmatropic rearrangements.
Recommended video:
Properties and Types of Pericyclic Reactions
Electrocyclic Reactions
Electrocyclic reactions are a type of pericyclic reaction where a conjugated system undergoes a ring closure or opening through the rotation of a sigma bond. The stereochemistry of the product depends on the thermal or photochemical conditions under which the reaction occurs, following the rules of orbital symmetry, specifically the Woodward-Hoffmann rules.
Recommended video:
Predicting Electrocyclic Products
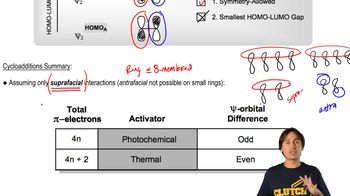
Cycloaddition Reactions
Cycloaddition reactions involve the formation of a cyclic compound by the addition of two or more unsaturated molecules. These reactions can be classified as [2+2] or [4+2] depending on the number of π bonds involved. Like electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions also adhere to the principles of orbital symmetry, influencing the reaction pathway and product formation.
Recommended video:
Cycloadditions Summary Chart
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 7:37m
7:37m