Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aldoses and Alditols
Aldoses are a type of monosaccharide that contain an aldehyde group, while alditols are sugar alcohols formed by the reduction of aldoses. The conversion of an aldose to an alditol typically involves the addition of hydrogen to the carbonyl group, resulting in a compound that lacks optical activity if it has a symmetrical structure.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - Reduction (Alditols)
Wohl Degradation
Wohl degradation is a chemical reaction that involves the conversion of aldoses into shorter-chain sugars. This process typically involves the oxidation of the aldose to form an intermediate, followed by a series of reactions that ultimately yield a new aldose with fewer carbon atoms, which can help identify the original aldose structure.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - Wohl Degradation
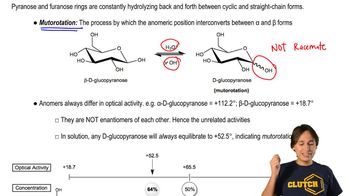
Optical Activity
Optical activity refers to the ability of a compound to rotate plane-polarized light, which is a characteristic of chiral molecules. A compound is optically inactive if it is either achiral or if it contains a plane of symmetry, resulting in the cancellation of optical activity. Understanding this concept is crucial for determining the stereochemistry of the aldoses and their derivatives in the given reactions.
Recommended video:
Mutorotation and Optical Activity
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 9:43m
9:43m