Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lactam Hydrolysis
Lactams are cyclic amides that can undergo hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks the amide bond, leading to the formation of a carboxylic acid and an amine. Understanding the structure of lactams and the conditions under which hydrolysis occurs is crucial for proposing a mechanism. The reaction typically involves nucleophilic attack by water, facilitated by a catalyst.
Recommended video:
Metal-Ion Catalysis
Metal-ion catalysis involves the use of metal ions to enhance the rate of a chemical reaction. In the context of lactam hydrolysis, metal ions can stabilize the transition state or activate the substrate, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack. Common metal ions used in catalysis include zinc, copper, and magnesium, which can coordinate with the lactam and facilitate the reaction.
Recommended video:
Metal Ion Catalysis Concept 1
Mechanistic Pathways
A mechanistic pathway outlines the step-by-step sequence of events that occur during a chemical reaction. For the metal-ion catalyzed hydrolysis of a lactam, it is essential to identify the key intermediates and transition states involved. This includes the initial coordination of the metal ion to the lactam, the nucleophilic attack by water, and the eventual breakdown of the lactam ring, leading to product formation.
Recommended video:
Energy Production In Biochemical Pathways Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: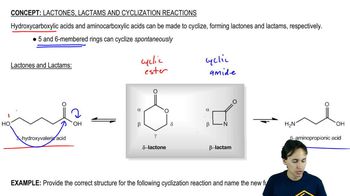


 5:53m
5:53m