Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Suzuki Coupling Reaction
The Suzuki coupling reaction is a widely used method in organic chemistry for forming carbon-carbon bonds. It involves the reaction of an organoboron compound with a halogenated organic compound in the presence of a palladium catalyst and a base. This reaction is particularly valuable for synthesizing biaryl compounds and other complex organic molecules.
Recommended video:
Organoboron Compounds
Organoboron compounds, such as boronic acids and esters, are key reactants in Suzuki coupling reactions. They contain a boron atom bonded to a carbon atom, which can participate in nucleophilic attack during the coupling process. Their reactivity and ability to form stable complexes with palladium make them essential for successful coupling reactions.
Recommended video:
Palladium Catalysis
Palladium catalysis is crucial in facilitating the Suzuki coupling reaction. The palladium catalyst, often in the form of Pd(PPh3)4, helps to activate the organoboron compound and the halide, allowing for the formation of the carbon-carbon bond. The choice of palladium catalyst and reaction conditions can significantly influence the efficiency and selectivity of the reaction.
Recommended video:
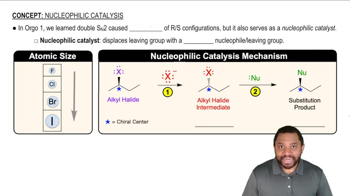
Nucleophilic Catalysis Concept 1

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 4:02m
4:02m