Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Claisen Condensation
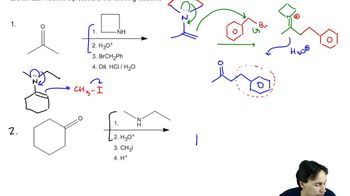
The Claisen condensation is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where two esters or an ester and a carbonyl compound react in the presence of a strong base to form a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. This reaction involves the nucleophilic attack of an enolate ion on the carbonyl carbon of another ester, leading to the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond.
Recommended video:
Enolate Ion Formation
Enolate ions are key intermediates in the Claisen condensation, formed when a strong base abstracts a proton from the α-carbon of an ester. This results in a resonance-stabilized anion that can act as a nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon of another ester or carbonyl compound, which is crucial for the reaction to proceed.
Recommended video:
Product Prediction
Predicting the product of a Claisen reaction involves understanding the structure of the starting materials and the mechanism of the reaction. The final product will typically be a β-keto ester or a β-diketone, depending on the reactants used. Analyzing the sterics and electronics of the reactants can also help in determining the major product formed.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution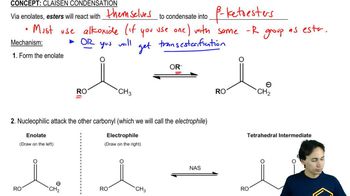


 6:08m
6:08m