Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cope Rearrangement
The Cope rearrangement is a thermal reaction involving the rearrangement of 1,5-hexadienes to form new isomeric products. This reaction is a sigmatropic rearrangement, where the movement of sigma bonds occurs in a concerted manner, typically resulting in a shift of the double bond positions. Understanding the mechanism and stereochemistry of this rearrangement is crucial for predicting the products accurately.
Recommended video:
Definition of Cope Rearrangement
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry refers to the study of the spatial arrangement of atoms in molecules and how this affects their chemical behavior. In the context of Cope reactions, the stereochemical configuration of the starting materials can influence the outcome of the reaction, leading to different stereoisomers. Recognizing the stereochemical implications is essential for predicting the correct product structure.
Recommended video:
Polymer Stereochemistry Concept 1
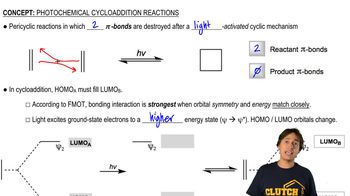
Thermal vs. Photochemical Reactions
Cope rearrangements are typically thermal reactions, meaning they occur at elevated temperatures without the need for light. This contrasts with photochemical reactions, which are driven by light energy. Understanding the conditions under which the Cope rearrangement occurs helps in predicting the reaction pathway and the stability of the products formed.
Recommended video:
MO Theory of Photochemical Cycloadditions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution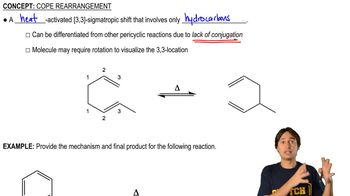


 6:28m
6:28m