Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds with the same molecular formula exhibit different structural or spatial arrangements. In the case of C4H8, isomers can be categorized into structural isomers, which differ in the connectivity of atoms, and stereoisomers, which have the same connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms. Understanding isomerism is crucial for identifying the various forms of a compound and their unique properties.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
NMR Spectroscopy
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. In proton NMR, the number of distinct hydrogen environments indicates the types of hydrogen atoms present, while in 13C NMR, the number of distinct carbon environments reveals the types of carbon atoms. Analyzing NMR data helps in deducing the molecular structure and understanding the compound's behavior in different environments.
Recommended video:
Chemical Environment
The chemical environment refers to the specific surroundings of an atom within a molecule, which influences its reactivity and NMR signals. In NMR spectroscopy, different types of hydrogen or carbon atoms can arise from variations in their bonding, hybridization, and neighboring groups. Recognizing how these environments affect NMR results is essential for interpreting spectra and determining the structure of unknown compounds.
Recommended video:
Chemical Reactions of Phosphate Anhydrides Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution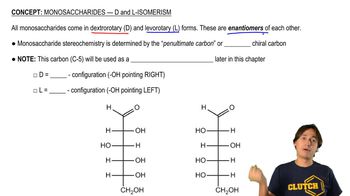



 4:m
4:m