Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chemical Shift
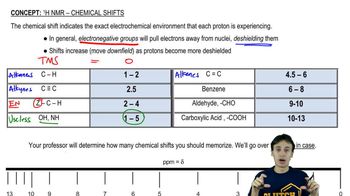
Chemical shift is a measure of the resonance frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard reference frequency, expressed in parts per million (ppm). It provides insight into the electronic environment surrounding the nucleus, allowing chemists to infer structural information about the molecule. In NMR spectroscopy, different functional groups resonate at different chemical shifts, which helps in identifying them.
Recommended video:
NMR Spectroscopy
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It exploits the magnetic properties of certain nuclei, such as hydrogen, when placed in a magnetic field and exposed to radiofrequency radiation. The frequency at which these nuclei resonate depends on their chemical environment, allowing for detailed analysis of molecular structure.
Recommended video:
Resonance Frequency Calculation
The resonance frequency of a proton in NMR can be calculated using the formula: frequency (MHz) = chemical shift (ppm) × spectrometer frequency (MHz). This relationship shows how the chemical shift translates into an actual frequency value based on the operating frequency of the NMR instrument. Understanding this calculation is essential for interpreting NMR data accurately.
Recommended video:
Drawing Resonance Structures