Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Tautomerization
Tautomerization is a chemical reaction that involves the rearrangement of atoms in a compound, typically involving the transfer of a proton and a shift of a double bond. In the case of vinyl alcohols, tautomerization leads to the formation of carbonyl compounds, where the hydroxyl group (-OH) is converted into a carbonyl group (C=O). This process is often rapid and reversible, highlighting the dynamic nature of certain organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms
Proton Transfer Mechanism
The proton transfer mechanism is a fundamental process in organic chemistry where a proton (H+) is transferred from one atom to another, facilitating various chemical transformations. In the isomerization of vinyl alcohol to carbonyl compounds, the proton transfer occurs from the hydroxyl group to an adjacent carbon atom, resulting in the formation of a double bond and the release of water. This mechanism is crucial for understanding the stability and reactivity of functional groups in organic molecules.
Recommended video:
Polyurethane Mechanism Example 1
Stability of Carbonyl Compounds
Carbonyl compounds, characterized by the presence of a carbon-oxygen double bond, are generally more stable than their corresponding vinyl alcohols. This stability arises from the resonance structures that can be drawn for carbonyls, which delocalize the electrons and lower the overall energy of the molecule. Understanding the stability of these compounds is essential for predicting the direction of isomerization reactions and the conditions under which they occur.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution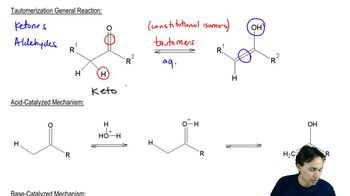



 1:51m
1:51m