Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Constitutional Isomers
Constitutional isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of their atoms. This means that the arrangement of atoms in the molecule varies, leading to different structural forms. Understanding constitutional isomers is crucial for recognizing how variations in structure can affect the properties and reactivity of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
Line-Angle Drawings
Line-angle drawings, also known as skeletal structures, are a shorthand way of representing organic molecules. In these drawings, carbon atoms are represented by the ends and intersections of lines, while hydrogen atoms are typically omitted for clarity. This method simplifies the visualization of complex structures, making it easier to identify isomers and their connectivity.
Recommended video:
Molecular Formula
A molecular formula indicates the number and types of atoms in a molecule, represented by the symbols of the elements and subscripts denoting the quantity of each atom. For example, C₆H₁₄ indicates a molecule with six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms. Understanding molecular formulas is essential for determining possible isomers and their structural variations.
Recommended video:
How to use IHD with molecular formula.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: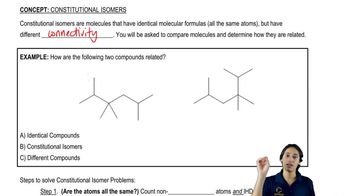



 1:10m
1:10m