Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It exploits the magnetic properties of certain nuclei, primarily hydrogen (¹H), to provide information about the number of hydrogen atoms in different environments within a molecule. The resulting spectrum displays peaks that correspond to these environments, allowing chemists to infer structural details.
Recommended video:
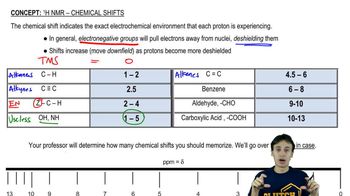
Chemical Shift
Chemical shift refers to the position of a peak in an NMR spectrum, measured in parts per million (ppm). It indicates the electronic environment surrounding the hydrogen atoms, influenced by factors such as electronegativity and hybridization. Different functional groups and molecular structures lead to distinct chemical shifts, which are crucial for identifying the types of hydrogen present in the molecule.
Recommended video:
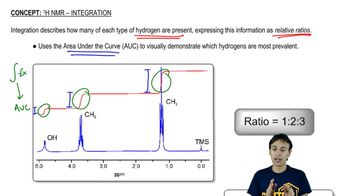
Integration and Multiplicity
Integration in NMR refers to the area under a peak, which correlates to the number of hydrogen atoms contributing to that signal. Multiplicity describes the splitting pattern of the peaks, which arises from the interaction of neighboring hydrogen atoms (n+1 rule). Understanding integration and multiplicity helps in determining the number of hydrogen atoms in different environments and their connectivity within the molecule.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution