Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nitrile Hydrolysis
Nitrile hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where a nitrile (R-C≡N) is converted into a carboxylic acid (R-COOH) through the addition of water. This reaction typically requires acidic or basic conditions to facilitate the breaking of the carbon-nitrogen triple bond. Understanding the mechanism of this reaction is crucial, as it involves nucleophilic attack by water and subsequent protonation steps.
Recommended video:
Review of Nitriles Concept 6
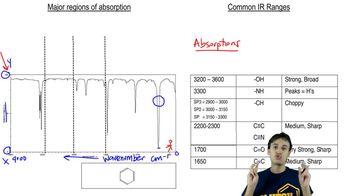
Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
Infrared spectroscopy (IR) is an analytical technique used to identify functional groups in organic compounds by measuring the absorption of infrared light. Different functional groups absorb characteristic wavelengths of IR radiation, producing distinct peaks in the spectrum. Analyzing the IR spectrum of the product can confirm the presence of a carboxylic acid, which would indicate whether the hydrolysis reaction occurred successfully.
Recommended video:
General Features of IR Spect
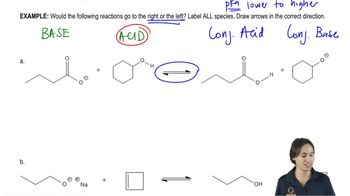
Reaction Conditions and Equilibrium
The conditions under which a chemical reaction occurs, including temperature and pressure, can significantly affect the reaction's rate and equilibrium position. In the case of nitrile hydrolysis, ambient heat may not provide sufficient energy to drive the reaction to completion. Understanding Le Chatelier's principle helps predict how changes in conditions can shift the equilibrium, which is essential for evaluating the chemist's hypothesis about the reaction's feasibility.
Recommended video:
Determining Acid/Base Equilibrium
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution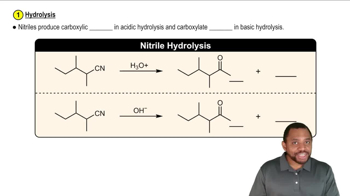

 12:6m
12:6m