Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
E/Z Isomerism
E/Z isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism that occurs in alkenes and other compounds with restricted rotation around a double bond. The 'E' (entgegen) configuration indicates that the highest priority substituents on each carbon of the double bond are on opposite sides, while the 'Z' (zusammen) configuration indicates they are on the same side. Understanding this concept is crucial for drawing and labeling the correct isomers.
Recommended video:
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Priority Rules
The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules are used to determine the priority of substituents attached to the double-bonded carbons in E/Z isomerism. According to these rules, the substituents are ranked based on the atomic number of the atoms directly attached to the double bond; higher atomic numbers receive higher priority. This ranking is essential for correctly identifying the E or Z configuration of the isomers.
Recommended video:
Why stereoisomers need their own naming system.
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry is the study of the spatial arrangement of atoms in molecules and how this affects their chemical properties and reactions. In the context of E/Z isomers, stereochemistry helps explain how different arrangements of substituents can lead to distinct physical and chemical properties, making it a fundamental concept for understanding isomerism in organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Polymer Stereochemistry Concept 1

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution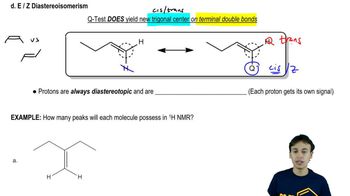



 1:10m
1:10m