Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Claisen–Schmidt Condensation
The Claisen–Schmidt condensation is a reaction between an aldehyde and a ketone in the presence of a base, leading to the formation of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound. This reaction involves the nucleophilic attack of the enolate ion derived from one carbonyl compound on the carbonyl carbon of the other, followed by dehydration. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for predicting the products formed in the synthesis of complex molecules like morachalcone A.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Compounds
Carbonyl compounds are organic molecules that contain a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O). They include aldehydes and ketones, which play significant roles in organic synthesis. In the context of the Claisen–Schmidt condensation, identifying the correct carbonyl compounds is essential, as their structure influences the reactivity and the final product of the reaction.
Recommended video:
Morachalcone A
Morachalcone A is a specific type of chalcone, a class of compounds characterized by a structure that includes two aromatic rings connected by a three-carbon α,β-unsaturated carbonyl system. Its synthesis often involves the strategic selection of carbonyl compounds to ensure the desired structural features are achieved. Understanding the target molecule's structure helps in determining the appropriate carbonyl precursors needed for its synthesis.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: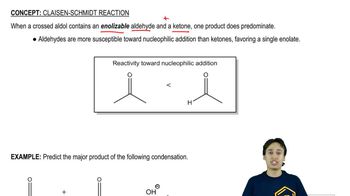


 2:10m
2:10m