Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Multiplicity in NMR Spectroscopy
Multiplicity refers to the number of peaks observed in a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum due to spin-spin coupling between neighboring nuclei. It indicates how many equivalent protons are adjacent to a given proton. For example, a triplet indicates that there are two neighboring protons, resulting in three peaks.
Recommended video:
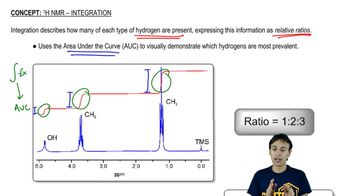
Integration in NMR
Integration in NMR spectroscopy quantifies the area under each peak, which corresponds to the number of protons contributing to that signal. The ratio of the integrals of the peaks provides insight into the relative number of protons in different environments, allowing chemists to deduce the structure of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Peak Ratio in Multiplicity
The peak ratio in a multiplicity pattern reflects the number of neighboring protons influencing the signal. For a triplet, the ratio of the peaks is typically 1:2:1, indicating that the central peak is twice as intense as the outer peaks. This pattern arises from the combinatorial ways the neighboring protons can align their spins with the observed proton.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 8:06m
8:06m