Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Systematic Naming of Organic Compounds
Systematic naming, or IUPAC nomenclature, is a standardized method for naming organic compounds based on their structure. It involves identifying the longest carbon chain, determining functional groups, and applying specific rules to create a unique name that conveys the compound's structure. Understanding this system is essential for accurately naming compounds like d-mannose.
Recommended video:
Name the following compound
Chirality and Asymmetric Centers
Chirality refers to the property of a molecule that makes it non-superimposable on its mirror image, often due to the presence of asymmetric centers, typically carbon atoms bonded to four different substituents. The configuration of these centers is designated as 'R' (rectus) or 'S' (sinister) based on the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules, which are crucial for determining the stereochemistry of compounds like d-mannose.
Recommended video:
Understanding Other Chiral Atoms
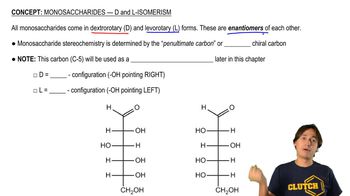
D-Mannose and Its Structure
D-mannose is a naturally occurring sugar and an epimer of glucose, specifically differing at one carbon atom. It is a six-carbon aldose with multiple asymmetric centers, making its stereochemistry important for its biological function. Recognizing its structure and how to derive its systematic name is vital for answering questions related to its configuration.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution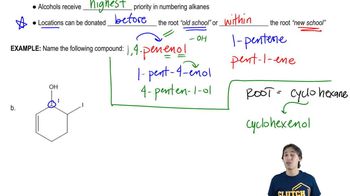


 3:11m
3:11m