Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Common Nomenclature in Organic Chemistry
Common nomenclature refers to the traditional names used for organic compounds, often based on their structure or functional groups. Unlike systematic IUPAC names, common names can be simpler and more widely recognized, such as 'ethyl alcohol' for ethanol. Understanding common names is essential for identifying and communicating about organic compounds effectively.
Recommended video:
What is an organic molecule?
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. Examples include hydroxyl (-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), and amino (-NH2) groups. Recognizing functional groups helps in determining the common names of compounds, as many common names are derived from these groups.
Recommended video:
Identifying Functional Groups
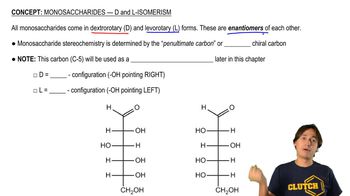
Structural Isomerism
Structural isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms. This can lead to different common names for isomers, as their properties and reactivity can vary significantly. Understanding structural isomerism is crucial for accurately naming and distinguishing between compounds in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism