Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Integration in NMR Spectroscopy
Integration in NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) spectroscopy refers to the area under the peaks in an NMR spectrum, which correlates to the number of protons contributing to that signal. This allows chemists to determine the relative number of hydrogen atoms in different environments within a molecule, aiding in structure elucidation.
Recommended video:
Multiplicity in NMR Spectroscopy
Multiplicity in NMR spectroscopy describes the splitting pattern of NMR signals, which arises from the interaction of neighboring hydrogen atoms (n+1 rule). This splitting provides information about the number of adjacent protons, helping to deduce the connectivity and arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Recommended video:
Alkyl Groups and Their NMR Patterns
Alkyl groups are hydrocarbon substituents derived from alkanes, and their NMR patterns vary based on their structure. For example, the t-butyl group (tert-butyl) has a unique NMR signature due to its three equivalent methyl groups, leading to a specific integration and multiplicity pattern that reflects its symmetrical structure.
Recommended video:
Common Splitting Patterns
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution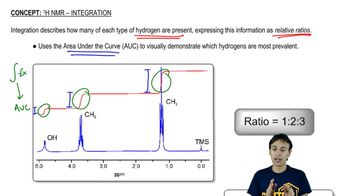



 6:46m
6:46m