Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In organic chemistry, recognizing functional groups such as ketones, alcohols, and halides is crucial for naming compounds and predicting their reactivity. For example, the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) indicates a ketone, while hydroxyl (-OH) signifies an alcohol.
Recommended video:
Identifying Functional Groups
IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method for naming organic chemical compounds. It provides a set of rules to create unique names based on the structure of the molecule, including the longest carbon chain, functional groups, and substituents. Understanding these rules is essential for accurately naming compounds, as seen in the provided structures, where the correct identification of functional groups influences the final name.
Recommended video:
The different parts of an IUPAC name
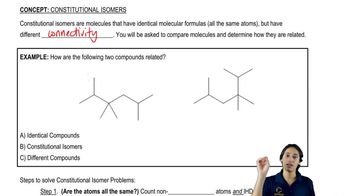
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms. This concept is important in organic chemistry as it affects the properties and reactivity of the compounds. For instance, the two structures in the question may represent different isomers, leading to distinct names and characteristics despite having the same number of atoms of each element.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 3:05m
3:05m