Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Tautomerization
Tautomerization is a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of a proton and a shift of a double bond, resulting in the interconversion between two isomers, known as tautomers. In organic chemistry, this often occurs between keto and enol forms, where the keto form contains a carbonyl group (C=O) and the enol form has a hydroxyl group (–OH) adjacent to a double bond. Understanding this process is crucial for predicting the stability and reactivity of compounds.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms
Enol Stability
The stability of enol tautomers can vary significantly based on factors such as hydrogen bonding, sterics, and resonance. Enols that can participate in intramolecular hydrogen bonding or have resonance stabilization are generally more stable. When analyzing enol tautomers, it is essential to evaluate these factors to determine which tautomer is favored under specific conditions, as this can influence the outcome of chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Keto-Enol Equilibrium
Keto-enol equilibrium refers to the dynamic balance between the keto and enol forms of a compound. The position of this equilibrium can be influenced by solvent effects, temperature, and the presence of catalysts. In many cases, the keto form is more thermodynamically stable, but certain conditions can favor the formation of the enol. Understanding this equilibrium is vital for predicting the behavior of compounds in various chemical environments.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution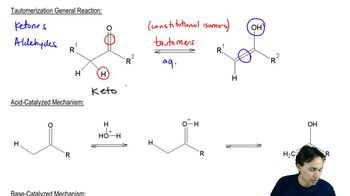



 1:51m
1:51m