Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aldohexoses
Aldohexoses are six-carbon sugars that contain an aldehyde group. They are a subclass of monosaccharides and include common sugars like glucose and galactose. The presence of the aldehyde functional group at one end of the molecule is crucial for their reactivity and classification as aldoses.
Recommended video:
Which aldohexoses produce the same Wohl Degradation product
Oxidation of Sugars
Oxidation of sugars involves the conversion of alcohol groups in the sugar molecule to carbonyl groups, resulting in the formation of acids. In the case of aldohexoses, the aldehyde group can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid, leading to the formation of aldaric acids. This process is significant in carbohydrate chemistry and can affect the properties and reactivity of the sugars.
Recommended video:
Aldaric Acids
Aldaric acids are dicarboxylic acids derived from the oxidation of both the aldehyde and the primary alcohol groups of aldohexoses. They have two carboxylic acid functional groups, one at each end of the carbon chain. Identifying pairs of aldohexoses that yield the same aldaric acid upon oxidation is important for understanding structural similarities and differences among sugars.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - Strong Oxidation (Aldaric Acid)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution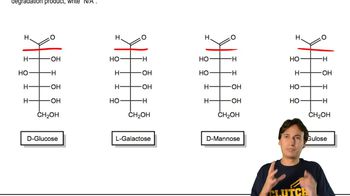



 3:10m
3:10m