Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pKa and Acidity
pKa is a measure of the acidity of a compound, indicating the strength of an acid in solution. A lower pKa value corresponds to a stronger acid, meaning it dissociates more readily to release protons (H+). Understanding pKa is essential for predicting the relative acidity of different compounds, such as cyclopropene and cyclopropane.
Recommended video:
Cyclopropene vs. Cyclopropane Structure
Cyclopropene (A) contains a double bond, while cyclopropane (B) is fully saturated with single bonds. The presence of the double bond in cyclopropene introduces strain and affects its stability and reactivity, which in turn influences its acidity. Recognizing the structural differences is crucial for predicting their pKa values.
Recommended video:
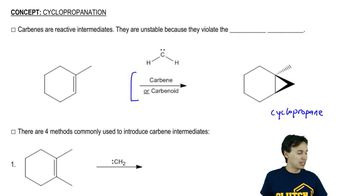
General properties of cyclopropanation.
Inductive and Resonance Effects
Inductive effects arise from the electronegativity of atoms, while resonance effects involve the delocalization of electrons across a molecule. In cyclopropene, the double bond can stabilize the conjugate base through resonance, potentially lowering its pKa compared to cyclopropane. Understanding these effects helps in predicting the relative acidity of the two compounds.
Recommended video:
Understanding the Inductive Effect.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 5:39m
5:39m