Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Tautomerism
Tautomerism is a chemical phenomenon where compounds exist in two or more interconvertible forms, typically differing in the position of a proton and a double bond. This is particularly relevant in organic chemistry, as it can affect the reactivity and properties of molecules. Tautomeric forms often include keto-enol or amine-imine pairs, and understanding this concept is crucial for predicting the behavior of nucleobases like cytosine, uracil, and guanine.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms
Aromaticity
Aromaticity refers to the enhanced stability and unique reactivity of cyclic compounds that follow Huckel's rule, which states that a molecule must have a planar structure with a specific number of π electrons (4n + 2) to be considered aromatic. This property is significant for nucleobases, as their aromatic rings contribute to their stability and interactions in biological systems, including base pairing in DNA and RNA.
Recommended video:
Hydroxy Groups
Hydroxy groups (-OH) are functional groups consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom. In the context of nucleobases, the presence of hydroxy groups can influence the tautomeric forms and the overall reactivity of the molecules. These groups can participate in hydrogen bonding, which is essential for the stability of nucleic acid structures and their interactions with other biomolecules.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: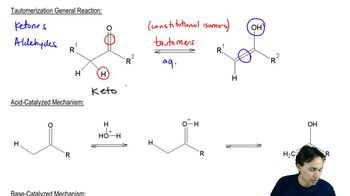



 0:29m
0:29m