Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
N-phthalimidomalonic ester synthesis
N-phthalimidomalonic ester synthesis is a method for synthesizing amino acids, particularly through the use of phthalimide and malonic ester. This reaction involves the formation of a phthalimide intermediate, which is then alkylated to introduce a side chain, followed by hydrolysis and decarboxylation to yield the final amino acid product.
Recommended video:
Synthesis of Amino Acids: N-Phthalimidomalonic Ester Synthesis Example 2
Alkyl halides
Alkyl halides are organic compounds containing a carbon chain bonded to a halogen atom (such as bromine, chlorine, or iodine). In the context of the N-phthalimidomalonic ester synthesis, the choice of alkyl halide influences the structure of the resulting amino acid, as it determines the side chain that will be attached to the amino acid backbone during the alkylation step.
Recommended video:
How to name alkyl halides
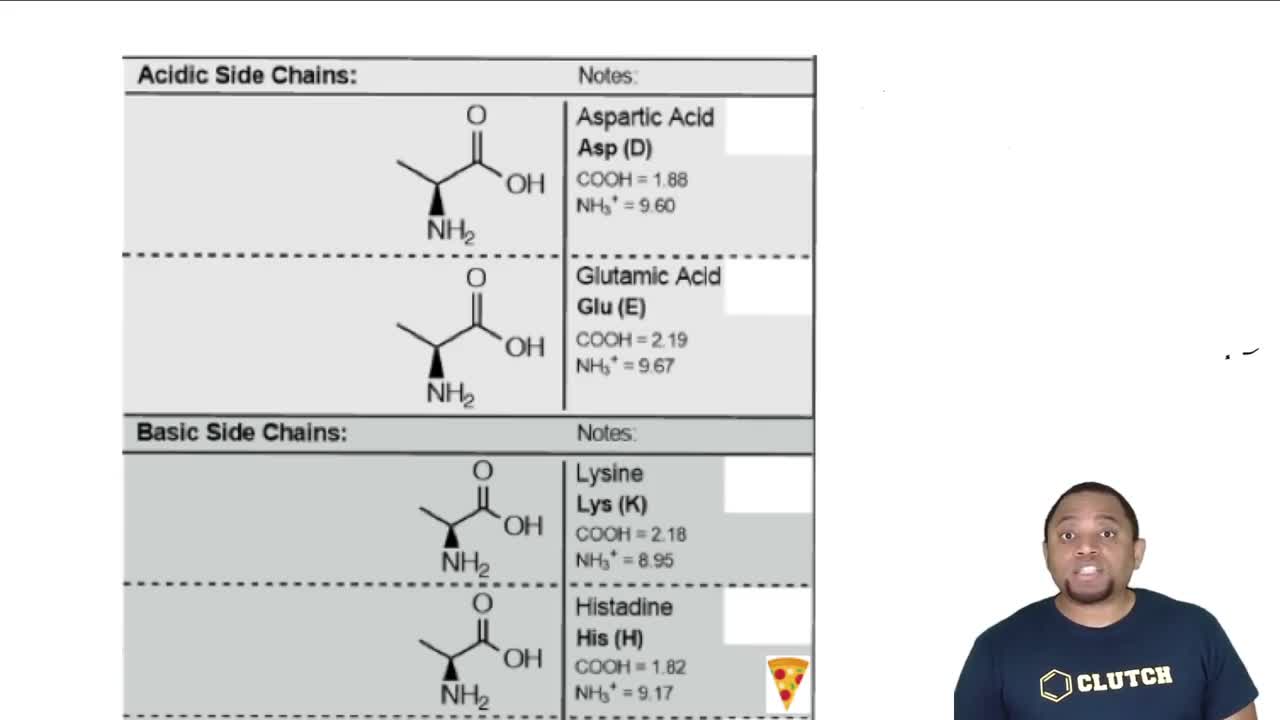
Amino acid structure
Amino acids are organic molecules that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group). The specific side chain determines the properties and identity of the amino acid, which is crucial for understanding how different alkyl halides will affect the final product in the synthesis process.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 3:11m
3:11m