Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isotope Labeling
Isotope labeling involves substituting a specific atom in a molecule with a heavier isotope, such as O-18 in this case. This technique allows chemists to trace the movement and incorporation of the labeled atom during chemical reactions. By analyzing the products, researchers can determine where the labeled atom ends up, providing insights into reaction mechanisms and pathways.
Recommended video:
Understanding the hydrogen isotopes.
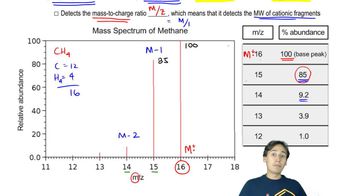
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It can identify the presence of isotopes in a compound by detecting differences in mass. In the context of the question, mass spectrometry can be employed to analyze the products of the reaction and confirm the presence of O-18, thus proving where the label appears in the final products.
Recommended video:
How to Read a Mass Spectrum
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It provides information about the environment of specific nuclei, including oxygen. By using NMR, one can identify the chemical shifts associated with the O-18 label, allowing for the determination of its location in the reaction products and confirming its incorporation into specific functional groups.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution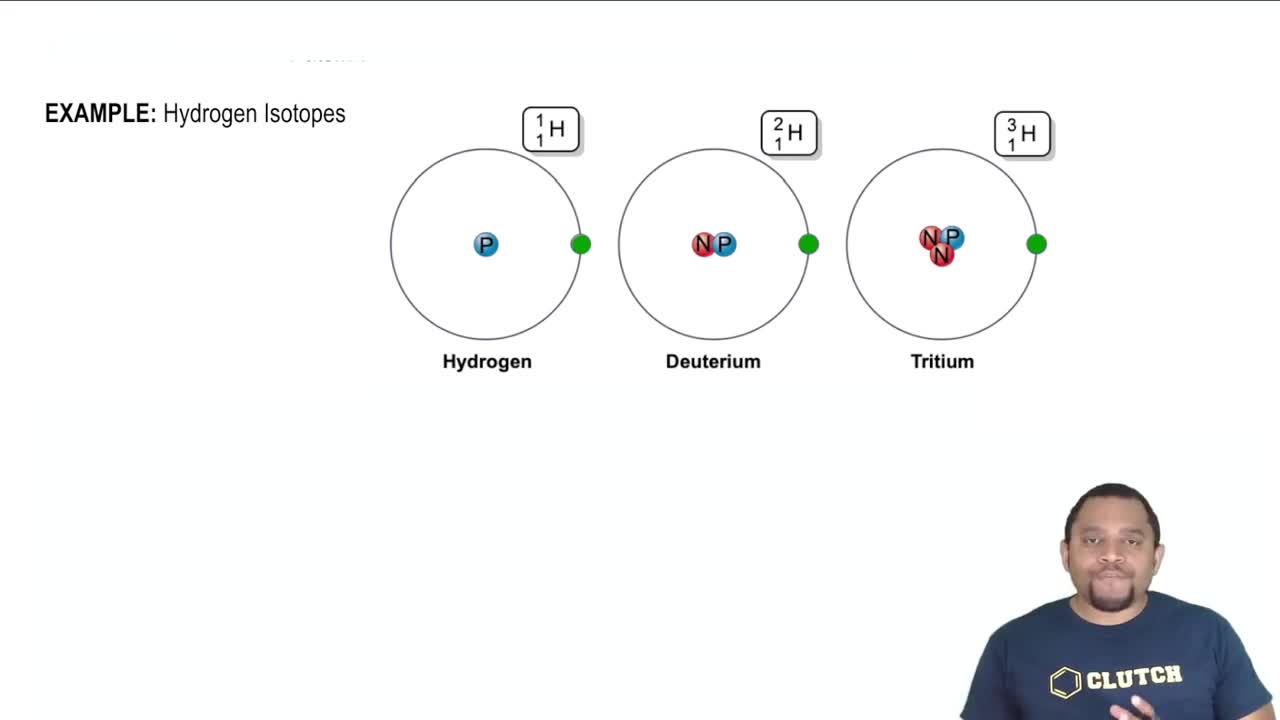


 1:48m
1:48m