Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkyl Halides
Alkyl halides are organic compounds containing a carbon atom bonded to a halogen atom (F, Cl, Br, or I). They are important in organic synthesis and can undergo various reactions, including nucleophilic substitution. Understanding the structure and reactivity of alkyl halides is crucial for predicting the products of reactions involving these compounds.
Recommended video:
How to name alkyl halides
Alkoxide Ions
Alkoxide ions are negatively charged species formed by deprotonation of alcohols. They are strong nucleophiles and are commonly used in organic reactions, such as the formation of ethers or in nucleophilic substitution reactions with alkyl halides. Recognizing the structure and reactivity of alkoxides is essential for understanding their role in organic synthesis.
Recommended video:
Metal Ion Catalysis Concept 1
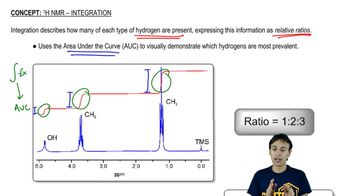
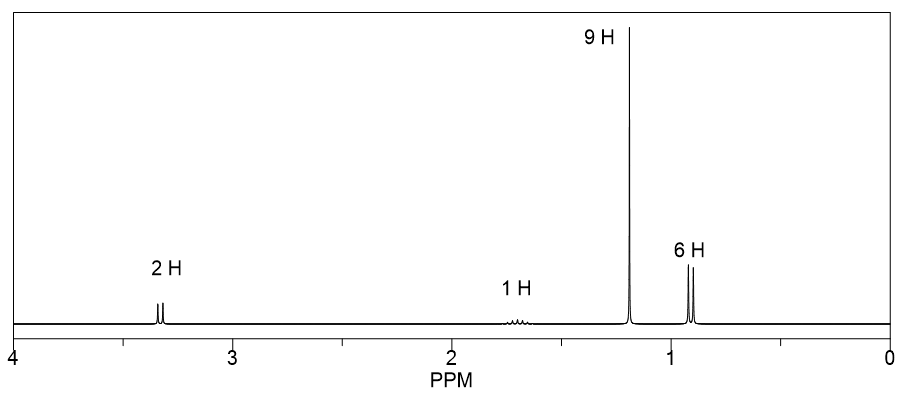
1H NMR Spectroscopy
1H NMR (proton nuclear magnetic resonance) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It provides information about the number of hydrogen atoms in different environments, allowing chemists to deduce molecular structure. Peaks in the NMR spectrum correspond to different hydrogen environments, and their integration reveals the relative number of protons, which is key to identifying the alkyl halide and alkoxide in the reaction.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution