Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Formula Interpretation
The molecular formula C6H10O indicates a compound containing six carbon atoms, ten hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom. Understanding the molecular formula is crucial for predicting the structure and reactivity of the compound. It provides insights into the degree of unsaturation, which can suggest the presence of double bonds or rings in the structure.
Recommended video:
How to use IHD with molecular formula.
DEPT 13C NMR Spectroscopy
DEPT (Distortionless Enhancement by Polarization Transfer) 13C NMR is a technique used to differentiate between carbon environments in organic compounds. It allows for the identification of CH3, CH2, and CH groups based on the intensity of the signals. This information is essential for deducing the structure of the compound by revealing how many of each type of carbon are present.
Recommended video:
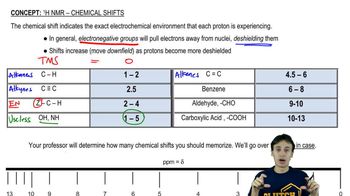
Chemical Shifts in NMR
Chemical shifts in NMR spectroscopy refer to the position of the peaks in the spectrum, measured in parts per million (ppm). Different types of carbon atoms resonate at different chemical shifts due to their electronic environments. For example, sp3 hybridized carbons (like those in CH3 and CH2 groups) typically appear in the 0-100 ppm range, while sp2 carbons (like those in alkenes) appear at higher ppm values, aiding in structural determination.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 4:m
4:m