Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons consisting only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms, connected by single bonds. They follow the general formula CnH2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes are characterized by their relatively low reactivity and are commonly found in natural gas and petroleum.
Recommended video:
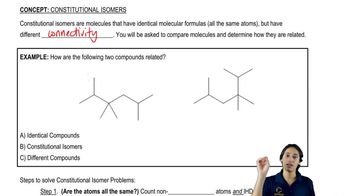
Constitutional Isomers
Constitutional isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of their atoms. This means that the arrangement of atoms in the molecule varies, leading to different structural forms. For C₆H₁₄, the five constitutional isomers include straight-chain and branched forms, showcasing the diversity of structures possible with the same number of atoms.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
Drawing Structural Formulas
Drawing structural formulas involves representing the arrangement of atoms in a molecule, including bonds between them. For alkanes, this means illustrating the carbon backbone and the hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon. Understanding how to depict these structures is essential for visualizing isomers and their unique properties.
Recommended video:
How to draw condensed mixed structures.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution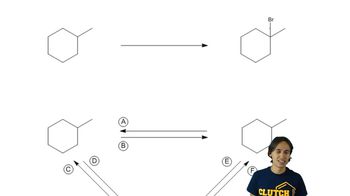


 1:10m
1:10m