Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cyclohexanecarbonyl Group
The cyclohexanecarbonyl group is derived from cyclohexane, where a carbonyl (C=O) functional group is attached to a carbon atom of the cyclohexane ring. This structure is important for understanding the reactivity and properties of the compound, as the carbonyl group is a key feature in many organic reactions, influencing both nucleophilic and electrophilic behavior.
Recommended video:
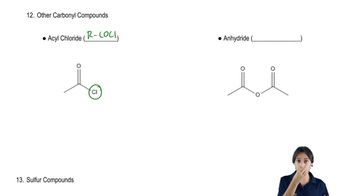
Acyl Chlorides
Acyl chlorides, also known as acid chlorides, are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) directly bonded to a chlorine atom. They are highly reactive and are commonly used in organic synthesis to form esters, amides, and other derivatives. Understanding their structure and reactivity is crucial for drawing and interpreting the structure of cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride.
Recommended video:
Recognizing acyl chlorides and anhydrides.
Structural Representation in Organic Chemistry
In organic chemistry, structural representation involves depicting the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, including bonds and functional groups. This can be done using various methods such as Lewis structures, condensed formulas, or skeletal structures. Accurately representing cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride requires knowledge of these conventions to convey the correct molecular geometry and functional groups present.
Recommended video:
What is an organic molecule?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 3:13m
3:13m