Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aldoses and Aldohexoses
Aldoses are a type of monosaccharide that contain an aldehyde group. Aldohexoses specifically refer to six-carbon aldoses, which include sugars like glucose and galactose. Understanding the structure and properties of these sugars is essential for determining the types of aldaric acids that can be derived from them.
Recommended video:
Which aldohexoses produce the same Wohl Degradation product
Aldaric Acids
Aldaric acids are dicarboxylic acids formed by the oxidation of both the aldehyde and the primary alcohol groups in aldoses. For each aldohexose, the oxidation leads to a unique aldaric acid, which retains the carbon skeleton of the original sugar. This concept is crucial for calculating the number of distinct aldaric acids that can be produced from the aldohexoses.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - Strong Oxidation (Aldaric Acid)
Isomerism in Sugars
Isomerism refers to the existence of compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. In the case of aldohexoses, there are multiple isomers due to variations in the arrangement of hydroxyl groups and the configuration around the chiral centers. Recognizing the different isomers is important for understanding how many unique aldaric acids can be formed from the 16 aldohexoses.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution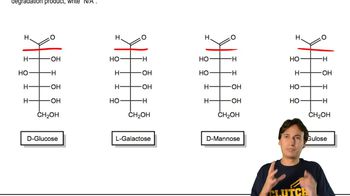



 3:10m
3:10m