Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amines
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They are classified based on the number of carbon-containing groups attached to the nitrogen atom: primary amines have one carbon group, secondary amines have two, and tertiary amines have three. Understanding the structure of amines is crucial for naming them systematically and identifying their classification.
Recommended video:
Systematic Naming
Systematic naming in organic chemistry follows the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) rules, which provide a standardized method for naming compounds. For amines, the name is derived from the longest carbon chain attached to the nitrogen, with the suffix '-amine' added. This systematic approach ensures clarity and consistency in identifying chemical structures.
Recommended video:
The different parts of an IUPAC name
Common Names
Common names are traditional names used for organic compounds that may not follow systematic naming conventions. They often reflect historical usage or structural features. For example, 'ethylamine' is a common name for a primary amine derived from ethane. Recognizing common names is important for understanding the broader context of chemical nomenclature and communication in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - Common Structures
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution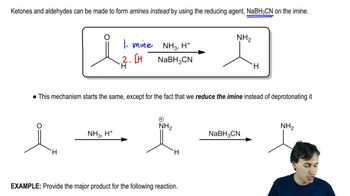


 6:50m
6:50m