Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It helps identify the composition of a sample by generating a mass spectrum, which displays the relative abundance of ions at different m/z (mass-to-charge) values. The molecular ion corresponds to the intact molecule, while fragment ions provide insights into the structure of the compound.
Recommended video:
How to Read a Mass Spectrum
Fragmentation Patterns
Fragmentation patterns refer to the specific ways in which a molecule breaks apart during mass spectrometry. Each hydrocarbon can produce characteristic fragment ions based on its structure, which can be used to deduce the molecular structure. The base peak represents the most abundant fragment, while other significant peaks indicate other common fragments that can help identify the compound.
Recommended video:
Common Splitting Patterns
Hydrocarbon Classification
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting solely of hydrogen and carbon atoms, classified into aliphatic (alkanes, alkenes, alkynes) and aromatic categories. Understanding the type of hydrocarbon is crucial for predicting its fragmentation behavior in mass spectrometry. The m/z values provided in the question can help narrow down the possible hydrocarbon structures based on known fragmentation patterns.
Recommended video:
Aromaticity of Hydrocarbons
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution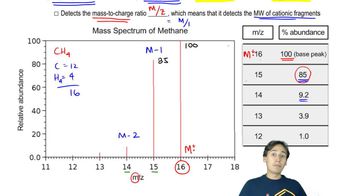



 1:48m
1:48m