Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Meso Compounds
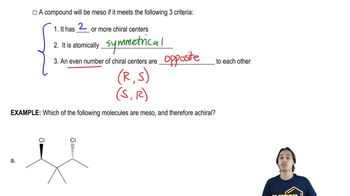
Meso compounds are a specific type of stereoisomer that possess multiple chiral centers but are achiral due to an internal plane of symmetry. This means that despite having chiral centers, the overall molecule does not exhibit optical activity because it can be superimposed on its mirror image.
Recommended video:
The 3 rules of meso compounds.
Chirality
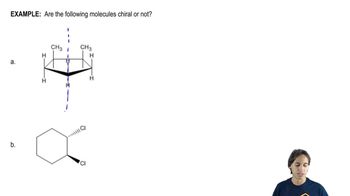
Chirality refers to the property of a molecule that makes it non-superimposable on its mirror image, much like left and right hands. A chiral molecule typically has at least one carbon atom bonded to four different substituents, leading to two possible configurations (enantiomers) that are mirror images of each other.
Recommended video:
Symmetry in Molecules
Symmetry in molecules plays a crucial role in determining their optical activity. A molecule with a plane of symmetry can be classified as achiral, even if it contains chiral centers. Identifying symmetry elements helps in recognizing meso compounds, as they will have a symmetrical arrangement that cancels out the chirality.
Recommended video:
Determining Chirality with Plane of Symmetry