After a proton is removed from the OH group, which compound in each pair forms a cyclic ether more rapidly?
c. <IMAGE>

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution
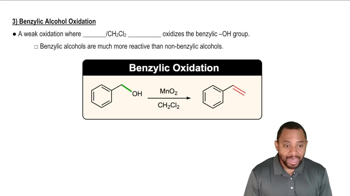
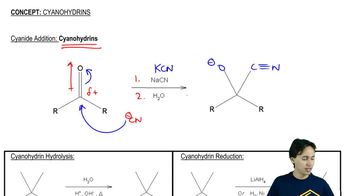

 2:27m
2:27mMaster Overview of the flowchart. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny Betancourt
Start learning