Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Spin-Spin Coupling
Spin-spin coupling refers to the interaction between nuclear spins of neighboring atoms in NMR spectroscopy. This interaction leads to the splitting of NMR signals into multiple peaks, known as multiplets, which provides information about the number of adjacent hydrogen atoms. The coupling constants (J values) quantify the strength of these interactions, influencing the pattern and spacing of the peaks.
Recommended video:
Sonogashira Coupling Reaction
Coupling Constants (J values)
Coupling constants, denoted as J, are measured in Hertz (Hz) and indicate the degree of interaction between coupled nuclei in NMR. They reflect the distance between the peaks in a split signal and are crucial for determining the number of neighboring protons. In this question, Jba = 12 Hz and Jbc = 6 Hz suggest different coupling strengths between the hydrogen atoms, which will affect the splitting pattern of Hb.
Recommended video:
Splitting without J-values
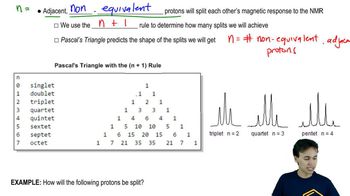
NMR Splitting Patterns
NMR splitting patterns arise from the interactions of a given hydrogen atom with its neighboring hydrogen atoms. The number of peaks in a splitting pattern is determined by the n+1 rule, where n is the number of neighboring protons. For Hb, the presence of Ha and Hc will create a specific splitting pattern based on their respective coupling constants, allowing for the visualization of the molecular environment around Hb.
Recommended video:
Common Splitting Patterns