Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Claisen Rearrangement
The Claisen rearrangement is a thermal reaction involving the rearrangement of allyl vinyl ethers to form γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. This reaction proceeds through a concerted mechanism, where the migration of the allyl group occurs simultaneously with the breaking and forming of bonds, resulting in a new carbon-carbon bond and a carbon-oxygen bond. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for predicting the products of the reaction shown.
Recommended video:
Definition of Claisen Rearrangement
Mechanistic Pathway
A mechanistic pathway outlines the step-by-step sequence of events that occur during a chemical reaction. In the context of the Claisen rearrangement, it involves the initial formation of a cyclic transition state, followed by the migration of the allyl group and the reformation of the double bond. Analyzing the mechanistic pathway helps in understanding the stability of intermediates and the overall energy changes during the reaction.
Recommended video:
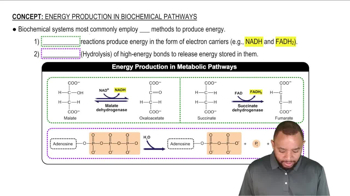
Energy Production In Biochemical Pathways Concept 1
Thermal Conditions
Thermal conditions refer to the temperature and heat applied during a chemical reaction, which can significantly influence the reaction rate and product formation. The Claisen rearrangement typically requires elevated temperatures to overcome the activation energy barrier. Recognizing the importance of thermal conditions is essential for optimizing reaction conditions and achieving desired yields in synthetic organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
MO Theory of Thermal Electrocyclics

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 6:08m
6:08m