Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Condensed Structural Formula
A condensed structural formula is a way of representing a chemical compound that shows the arrangement of atoms and the connectivity between them without depicting all the bonds explicitly. In this format, groups of atoms are often grouped together, and hydrogen atoms attached to carbons are usually omitted for simplicity. This representation helps in visualizing the molecular structure while maintaining clarity.
Recommended video:
How to interpret condensed structures.
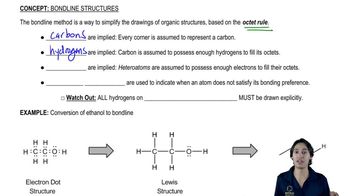
Skeletal Structure
A skeletal structure, also known as a line-angle structure, is a simplified representation of a molecule where carbon atoms are represented by vertices or ends of lines, and hydrogen atoms are implied. This format emphasizes the connectivity of the carbon backbone and functional groups, making it easier to visualize larger organic molecules. It is particularly useful for complex structures, as it reduces clutter and focuses on the essential features.
Recommended video:
How bondline is different from Lewis Structures.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In organic chemistry, identifying functional groups is crucial for understanding the properties and reactivity of compounds. For example, in sec-butylamine, the amine group (-NH2) is the functional group that influences its behavior, while in isopentyl bromide, the bromine atom serves as a leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Recommended video:
Identifying Functional Groups
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution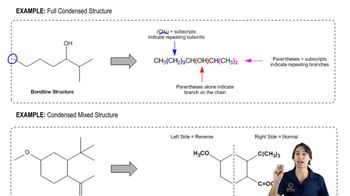


 6:50m
6:50m