Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amide Chemistry
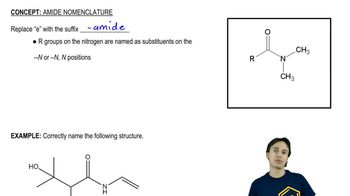
Amides are organic compounds derived from carboxylic acids and amines, characterized by the functional group -C(=O)N-. They serve as versatile intermediates in organic synthesis, allowing for the transformation of carboxylic acids into amines or other nitrogen-containing compounds through various reactions, such as reduction or alkylation.
Recommended video:
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Nucleophilic substitution reactions involve the replacement of a leaving group in a molecule with a nucleophile. In the context of amides, this can include the alkylation of the nitrogen atom, where a nucleophile attacks the carbon atom of the amide, leading to the formation of new amines or substituted amides, which is crucial for synthesizing compounds like benzyldimethylamine.
Recommended video:
Nucleophiles and Electrophiles can react in Substitution Reactions.
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Carboxylic acid derivatives, such as esters, amides, and anhydrides, can be transformed into one another through various chemical reactions. Understanding these derivatives is essential for the synthesis of compounds like cyclopentanecarbonitrile from cyclopentanecarboxylic acid, as they dictate the reactivity and pathways available for functional group transformations.
Recommended video:
Intro to Carboxylic Acid Derivatives