Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chemical Equivalence
Chemical equivalence refers to protons in a molecule that are in identical environments, leading to them having the same chemical shift in NMR spectroscopy. In the context of the provided structure, identifying sets of equivalent protons is crucial for determining their respective signals in the 1H NMR spectrum.
Recommended video:
Chemical Reactions of Phosphate Anhydrides Concept 1
NMR Multiplicity
Multiplicity in NMR refers to the splitting of signals due to spin-spin coupling between neighboring protons. The number of peaks in a signal is determined by the n+1 rule, where n is the number of neighboring protons. Understanding multiplicity helps in interpreting the complexity of the NMR spectrum and the connectivity of protons in the molecule.
Recommended video:
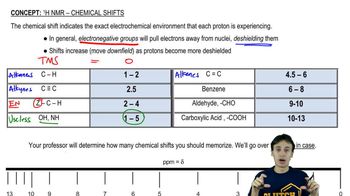
Chemical Shift
Chemical shift is the position of an NMR signal, measured in parts per million (ppm), which indicates the electronic environment surrounding a proton. Factors such as electronegativity of nearby atoms and hybridization affect chemical shifts. Recognizing the chemical shifts of different proton environments is essential for predicting the order of signals in the NMR spectrum.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 12:21m
12:21m