Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chair Conformation
The chair conformation is a three-dimensional representation of cyclohexane and its derivatives, which minimizes steric strain and torsional strain. In this conformation, carbon atoms are arranged in a staggered manner, allowing for more stable interactions between substituents. Understanding chair conformations is crucial for visualizing the spatial arrangement of atoms in cyclic compounds.
Recommended video:
What is a chair conformation?
Cis and Trans Isomerism
Cis and trans isomerism refers to the different spatial arrangements of substituents around a double bond or a ring structure. In the context of cyclohexane derivatives, 'cis' indicates that substituents are on the same side of the ring, while 'trans' indicates they are on opposite sides. This distinction affects the physical and chemical properties of the compounds, making it essential for predicting reactivity and stability.
Recommended video:
Is the following cyclohexane cis or trans?
Planar Representation
Planar representation is a two-dimensional depiction of a three-dimensional molecular structure, often used to simplify the visualization of complex molecules. When converting chair conformations to planar forms, it is important to accurately represent the relative positions of substituents to maintain the correct stereochemistry. This skill is vital for understanding molecular interactions and reactivity in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
Rules for Predicting Planarity

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution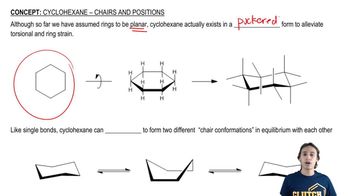



 1:18m
1:18m