Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
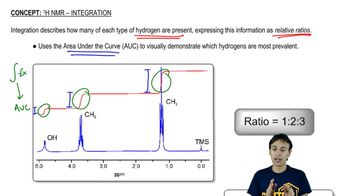
1H NMR Spectroscopy
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It provides information about the number of hydrogen atoms in different environments within a molecule, indicated by peaks in the spectrum. The position of these peaks (chemical shifts) reveals the electronic environment of the protons, while the area under each peak corresponds to the number of protons contributing to that signal.
Recommended video:
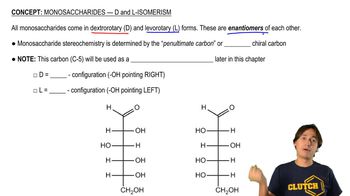
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural or spatial arrangements. In the case of C7H14O, the isomers can differ in the arrangement of carbon chains, functional groups, or stereochemistry. Understanding isomerism is crucial for interpreting NMR spectra, as different isomers will produce distinct patterns of peaks due to variations in their hydrogen environments.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
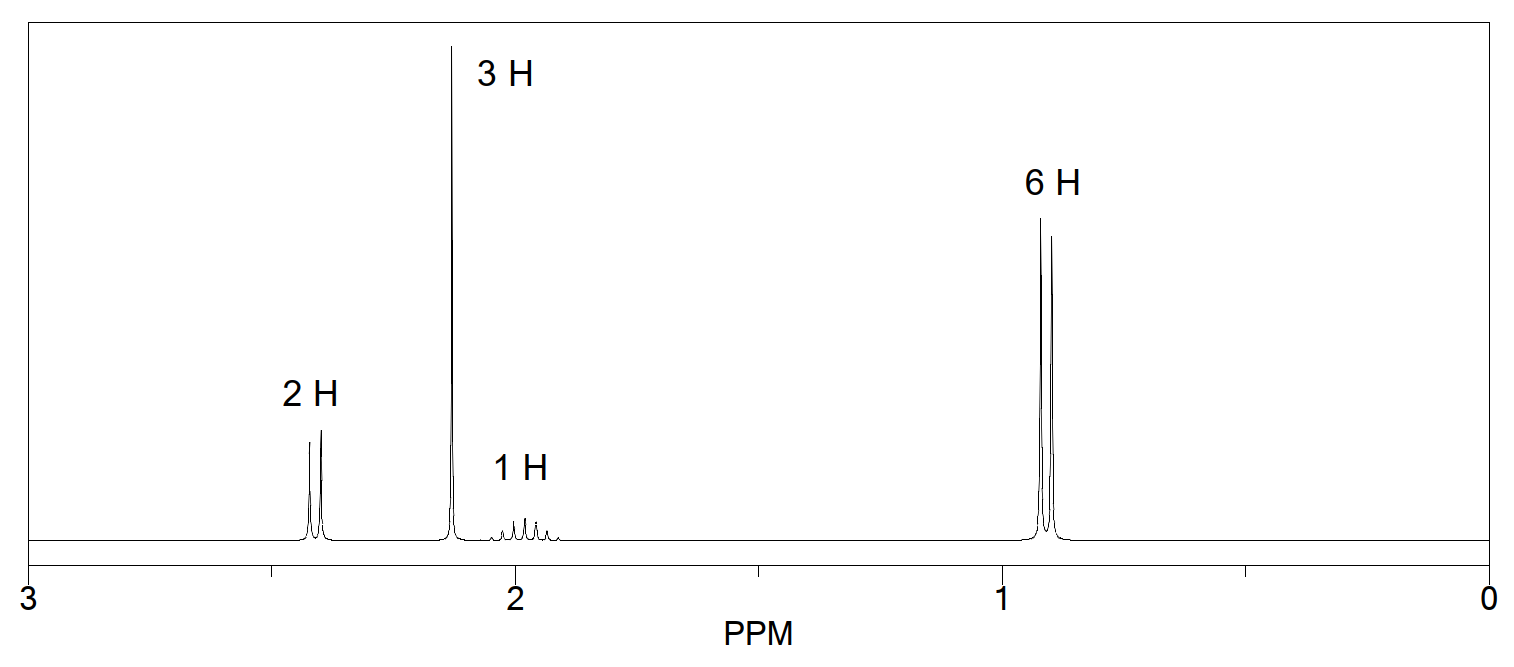
Integration in NMR
Integration in NMR spectroscopy involves measuring the area under the peaks in the spectrum, which correlates to the number of protons contributing to each signal. This allows chemists to deduce the relative number of hydrogen atoms in different environments. For example, in the provided spectrum, the integration values (1 H, 2 H, 6 H) indicate how many protons are associated with each peak, aiding in the identification of the corresponding isomers.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution