Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerization
Isomerization is a chemical process where a compound is transformed into another compound with the same molecular formula but a different structural arrangement. In the context of sugars, isomerization can occur between ketoses and aldoses, affecting their reactivity and properties. Understanding this process is crucial for predicting how sugars behave under different conditions.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
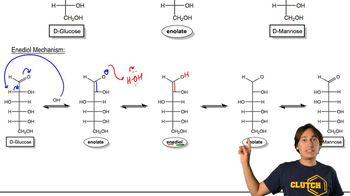
Enediol Intermediate
An enediol intermediate is a species that contains a carbon-carbon double bond adjacent to a hydroxyl group. This structure is pivotal in the isomerization of sugars, as it allows for the interconversion between different forms of sugars, such as ketoses and aldoses. The stability and reactivity of the enediol can significantly influence the reaction pathway.
Recommended video:
Enolate Ion
An enolate ion is a resonance-stabilized anion formed by the deprotonation of a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl group. In the isomerization of sugars, the formation of different enolate ions from the enediol intermediate can lead to distinct reaction pathways and products. Understanding the formation and reactivity of enolate ions is essential for predicting the outcomes of sugar isomerization.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution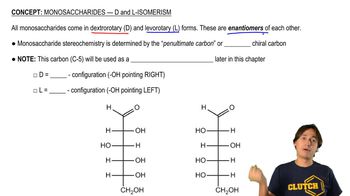


 3:21m
3:21m