Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Formula
A molecular formula represents the number and types of atoms in a molecule. It is expressed using chemical symbols and subscripts, indicating how many of each atom are present. For example, C6H12O6 denotes a molecule with six carbon, twelve hydrogen, and six oxygen atoms. Understanding molecular formulas is crucial for determining the composition of compounds and predicting their properties.
Recommended video:
How to use IHD with molecular formula.
Nitrogen in Organic Compounds
Nitrogen is a common element in organic chemistry, often found in amines, amides, and other functional groups. Its presence can significantly affect the chemical behavior and reactivity of a compound. For instance, nitrogen can participate in hydrogen bonding, influencing solubility and boiling points. Recognizing how nitrogen integrates into molecular structures is essential for analyzing organic compounds.
Recommended video:
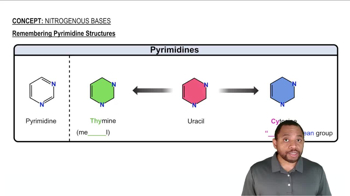
Nitrogenous Bases Concept 2
Valency and Bonding
Valency refers to the ability of an atom to bond with other atoms, determined by the number of electrons in its outer shell. Nitrogen, with a valency of three, typically forms three covalent bonds, allowing it to connect with various elements, including carbon and hydrogen. Understanding valency is fundamental for predicting how atoms combine to form stable molecules, particularly in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
What is a valence electron?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:48m
1:48m